-
Welcome to Tamil Brahmins forums.
You are currently viewing our boards as a guest which gives you limited access to view most discussions and access our other features. By joining our Free Brahmin Community you will have access to post topics, communicate privately with other members (PM), respond to polls, upload content and access many other special features. Registration is fast, simple and absolutely free so please, join our community today!
If you have any problems with the registration process or your account login, please contact contact us.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Mobiles can cause Brain Tumor - Dr.B.M.Hegde latest speech
- Thread starter drsundaram
- Start date
prasad1
Active member
Is there any link between cellphones and cancer?
Answer From Edward T. Creagan, M.D.
The possible connection between cellphones and cancer is controversial. Many years' worth of studies on cellphones and cancer have yielded conflicting results. Currently, there's no consensus about the degree of cancer risk — if any — posed by cellphone use.
The primary concern with cellphones and cancer seems to be the development of brain tumors associated with cellphone use. Some research suggests a slight increase in the rate of brain tumors since the 1970s, but cellphones weren't in use during the 1970s.
Instead, the subtle increases are more likely related to other factors — such as increased access to medical care and improvements in diagnostic imaging.
Still, a series of recent studies can't tell the entire story. It often takes many years between the use of a new cancer-causing agent and the observation of an increase in cancer rates, such as with tobacco and lung cancer. At this point, it's possible that too little time has passed to detect an increase in cancer rates directly attributable to cellphone use.
For now, no one knows if cellphones are capable of causing cancer. Although long-term studies are ongoing, to date there's no convincing evidence that cellphone use increases the risk of cancer. If you're concerned about the possible link between cellphones and cancer, consider limiting your use of cellphones — or use a speaker or hands-free device that places the cellphone antenna, which is typically in the cellphone itself, away from your head.

 www.mayoclinic.org
www.mayoclinic.org
Answer From Edward T. Creagan, M.D.
The possible connection between cellphones and cancer is controversial. Many years' worth of studies on cellphones and cancer have yielded conflicting results. Currently, there's no consensus about the degree of cancer risk — if any — posed by cellphone use.
The primary concern with cellphones and cancer seems to be the development of brain tumors associated with cellphone use. Some research suggests a slight increase in the rate of brain tumors since the 1970s, but cellphones weren't in use during the 1970s.
Instead, the subtle increases are more likely related to other factors — such as increased access to medical care and improvements in diagnostic imaging.
- In one study that followed more than 420,000 cellphone users over a 20-year period, researchers found no evidence of a link between cellphones and brain tumors.
- Another study found an association between cellphones and cancer of the salivary glands. However, only a small number of study participants had malignant tumors.
- Another study suggested a possible increased risk of glioma — a specific type of brain tumor — for the heaviest cellphone users, but no increase in brain tumor risk overall.
Still, a series of recent studies can't tell the entire story. It often takes many years between the use of a new cancer-causing agent and the observation of an increase in cancer rates, such as with tobacco and lung cancer. At this point, it's possible that too little time has passed to detect an increase in cancer rates directly attributable to cellphone use.
For now, no one knows if cellphones are capable of causing cancer. Although long-term studies are ongoing, to date there's no convincing evidence that cellphone use increases the risk of cancer. If you're concerned about the possible link between cellphones and cancer, consider limiting your use of cellphones — or use a speaker or hands-free device that places the cellphone antenna, which is typically in the cellphone itself, away from your head.

Is there a connection between cellphones and cancer?
A Mayo Clinic specialist discusses the controversial topic of cellphones and cancer.
prasad1
Active member
Exposure to ionizing radiation, such as from x-rays, is known to increase the risk of cancer. However, although many studies have examined the potential health effects of non-ionizing radiation from radar, microwave ovens, cell phones, and other sources, there is currently no consistent evidence that non-ionizing radiation increases cancer risk in humans.
The only consistently recognized biological effect of radiofrequency radiation in humans is heating. The ability of microwave ovens to heat food is one example of this effect of radiofrequency radiation. Radiofrequency exposure from cell phone use does cause heating to the area of the body where a cell phone or other device is held (e.g., the ear and head). However, it is not sufficient to measurably increase body temperature. There are no other clearly established effects on the human body from radiofrequency radiation.
What can cell phone users do to reduce their exposure to radiofrequency radiation?
The FDA has suggested some steps that concerned cell phone users can take to reduce their exposure to radiofrequency radiation (49):

 www.cancer.gov
www.cancer.gov
The only consistently recognized biological effect of radiofrequency radiation in humans is heating. The ability of microwave ovens to heat food is one example of this effect of radiofrequency radiation. Radiofrequency exposure from cell phone use does cause heating to the area of the body where a cell phone or other device is held (e.g., the ear and head). However, it is not sufficient to measurably increase body temperature. There are no other clearly established effects on the human body from radiofrequency radiation.
What can cell phone users do to reduce their exposure to radiofrequency radiation?
The FDA has suggested some steps that concerned cell phone users can take to reduce their exposure to radiofrequency radiation (49):
- Reserve the use of cell phones for shorter conversations or for times when a landline phone is not available.
- Use a device with hands-free technology, such as wired headsets, which place more distance between the phone and the head of the user.

Cell Phones and Cancer Risk Fact Sheet
A fact sheet that outlines the available evidence regarding use of cellular/mobile telephones and cancer risk.
prasad1
Active member
The Million Women Study
A large prospective (forward-looking) study of nearly 800,000 women in the UK examined the risk of developing brain tumors over a 7-year period in relation to self-reported cell phone use at the start of the study. This study found no link between cell phone use and brain tumors overall or several common brain tumor subtypes, but it did find a possible link between long-term cell phone use and acoustic neuromas.
According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI):
“Studies thus far have not shown a consistent link between cell phone use and cancers of the brain, nerves, or other tissues of the head or neck. More research is needed because cell phone technology and how people use cell phones have been changing rapidly.”
 www.cancer.org
www.cancer.org
A large prospective (forward-looking) study of nearly 800,000 women in the UK examined the risk of developing brain tumors over a 7-year period in relation to self-reported cell phone use at the start of the study. This study found no link between cell phone use and brain tumors overall or several common brain tumor subtypes, but it did find a possible link between long-term cell phone use and acoustic neuromas.
According to the National Cancer Institute (NCI):
“Studies thus far have not shown a consistent link between cell phone use and cancers of the brain, nerves, or other tissues of the head or neck. More research is needed because cell phone technology and how people use cell phones have been changing rapidly.”
Do Cell Phones Cause Cancer? | Cellphones and Cancer
. Learn what is known about the possible link between cell phone use and cancer.
prasad1
Active member
The supposed health risk from mobile phones is the story that will never die. The latest claim, branded an “inconvenient truth” by the Observer newspaper, is that new research shows they cause cancer in rats. But like all previous incarnations of this tale, the real truth is that the evidence has been overblown and there is nothing to worry about.
Read more: https://www.newscientist.com/articl...ill-wont-give-you-brain-cancer/#ixzz6AiyoIPRL
Read more: https://www.newscientist.com/articl...ill-wont-give-you-brain-cancer/#ixzz6AiyoIPRL
prasad1
Active member
When making safety recommendations, public health officials typically place more weight on evidence from human studies or trials. In the case of cell phones, several large human studies have been conducted to analyze the potential link between cell phone use and brain cancer. Typically, these are studies in which individuals with brain tumors are surveyed about their cell phone use and compared with individuals without brain tumors. Overall, these studies do not show a link between cell phone use and cancer.
“Any individual study might find something unusual,” Dr. Dauer says. “But what’s most important to consider is the weight of evidence across all of them.” And that, he says, does not show any clear link between cell phones and cancer.
Nor do the available data on cancer incidence show that rates of brain cancer are increasing.
“A questioning scientist might say, ‘Well, we just haven’t used them long enough to see an effect on cancer rates.’ That’s why it’s important to continue to study this,” he adds.
An ongoing study called COSMOS that is being conducted in several European countries is following cell phone users for 20 to 30 years.

 www.mskcc.org
www.mskcc.org
“Any individual study might find something unusual,” Dr. Dauer says. “But what’s most important to consider is the weight of evidence across all of them.” And that, he says, does not show any clear link between cell phones and cancer.
Nor do the available data on cancer incidence show that rates of brain cancer are increasing.
“A questioning scientist might say, ‘Well, we just haven’t used them long enough to see an effect on cancer rates.’ That’s why it’s important to continue to study this,” he adds.
An ongoing study called COSMOS that is being conducted in several European countries is following cell phone users for 20 to 30 years.

Do Cell Phones Cause Cancer?
We love our smartphones, but could they be harming our health? An MSK expert weighs in.
prasad1
Active member
Summary
Mobile phones are in widespread use and so it is important to continue to investigate and monitor any potential public health impact. Although there remains some uncertainty, current scientific evidence indicates that a link between typical mobile phone use or mobile base stations and cancer is unlikely. There is inconsistent evidence to suggest that very heavy users of mobile phones may have a slightly increased risk of cancer.

 www.cancerwa.asn.au
www.cancerwa.asn.au
As usual, Dr. Hegde is late to the discussion but has a big megaphone.
Mobile phones are in widespread use and so it is important to continue to investigate and monitor any potential public health impact. Although there remains some uncertainty, current scientific evidence indicates that a link between typical mobile phone use or mobile base stations and cancer is unlikely. There is inconsistent evidence to suggest that very heavy users of mobile phones may have a slightly increased risk of cancer.

Mobile phones and cancer-cancer myth - Cancer Council Western Australia
Information relating to the myth about the link between mobile phones and cancer
As usual, Dr. Hegde is late to the discussion but has a big megaphone.
prasad1
Active member
The truth about mobile phones and cancer
A scientist tells BBC’s “Truth or Scare” the amount of radio waves emitted by mobile phones is so small, it doesn’t damage cells in our bodies. They found no evidence that should cause worry.
Why, then do we see more brain tumors? Is it mere coincidence that brain cancer has increased at the same time cellphone usage has?
The reason we’ve seen more diagnoses of brain cancers is because the scientific community has gotten better at detecting cancers, the BBC scientist says. In fact, they point out that the most significant health risk of mobile phones is distracted driving (and distracted walking).
Research about mobile phones and cancer
In the United Kingdom, brain cancer diagnoses have increased 34% over the past 20 years. But, as Cancer Research UK (CRUK) points out, cell phone ownership in the UK rose by 500% between 1990 and 2016. So if phones were to blame for the increase, CRUK researchers say the rate of brain cancer would be much higher.
In the U.S., the National Cancer Institute tells us there are three reasons that make us worry about cell phones and brain cancer:

 www.komando.com
www.komando.com
Dr. Hegede has the habit of making a mountain out of a molehill.
A scientist tells BBC’s “Truth or Scare” the amount of radio waves emitted by mobile phones is so small, it doesn’t damage cells in our bodies. They found no evidence that should cause worry.
Why, then do we see more brain tumors? Is it mere coincidence that brain cancer has increased at the same time cellphone usage has?
The reason we’ve seen more diagnoses of brain cancers is because the scientific community has gotten better at detecting cancers, the BBC scientist says. In fact, they point out that the most significant health risk of mobile phones is distracted driving (and distracted walking).
Research about mobile phones and cancer
In the United Kingdom, brain cancer diagnoses have increased 34% over the past 20 years. But, as Cancer Research UK (CRUK) points out, cell phone ownership in the UK rose by 500% between 1990 and 2016. So if phones were to blame for the increase, CRUK researchers say the rate of brain cancer would be much higher.
In the U.S., the National Cancer Institute tells us there are three reasons that make us worry about cell phones and brain cancer:
- Cell phones emit radio-frequency radiation from their antennas. The head is nearest to the antenna.
- The number of cell phone users has increased rapidly.
- The time we spend on cell phones has increased.

Do mobile phones cause brain cancer?
The connection between cellphones and cancer has been debated for decades. The truth is, it's complicated. Here's a roundup of what scientists say about the connection between mobile phones and brain cancer.
Dr. Hegede has the habit of making a mountain out of a molehill.
prasad1
Active member
There are many cancer myths that haven’t been proven to cause cancer. However, there are proven causes of cancer, and things you can do to reduce your risk. Follow this link to find out more.
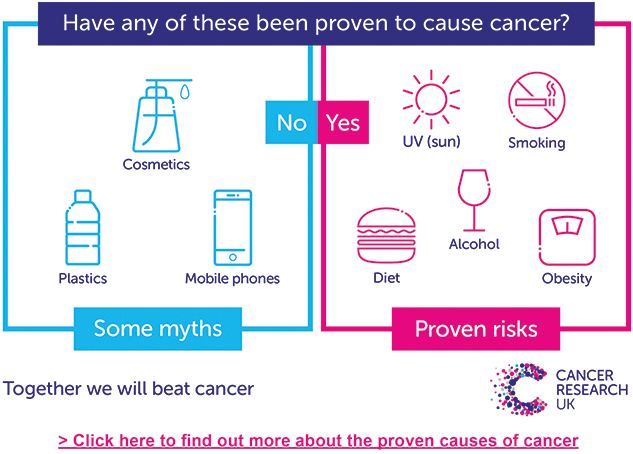
 www.cancerresearchuk.org
www.cancerresearchuk.org

Do mobile phones, 4G or 5G cause cancer?
Mobile phones, 4G and 5G do not increase the risk of cancer in humans.
Latest ads
-
For rent [Property for Rent] 2 bhk for rent2 bhk rent in Thiruvanmiyur chennai
- tbs (+0 /0 /-0)
- Updated:
-
Wanted Wanted female Brahmin cook and caretaker in CoimbatoreNeed a female Brahmin cook and caretaker in Kovaipudur, Coimbatore
- Peace$ (+0 /0 /-0)
- Updated:
- Expires
-
Wanted [Want to Buy] Property close to Perumal TemplePlanning to create a nandavanam for pushpa kainkaryam of Perumal.
- Balamuruganpulsars (+0 /0 /-0)
- Updated:
- Expires
-
-
For rent FOR RENT-Kolathur, 2 BHK 16000rs. onlyBrand new 2 Bedroom house for rent in kolathur_16000
- sang (+0 /0 /-0)
- Updated:
- Expires
